Why is preventive screening for cervical cancer important?
HPV infections, even when they do not cause symptoms, can, under certain conditions, develop into cervical cancer. Usually, this takes 10-15 years. The goal of preventive screening is to diagnose cervical lesions that either require more frequent patient follow-up or even treatment before they lead to cancer.
How is preventive screening for cervical cancer performed?
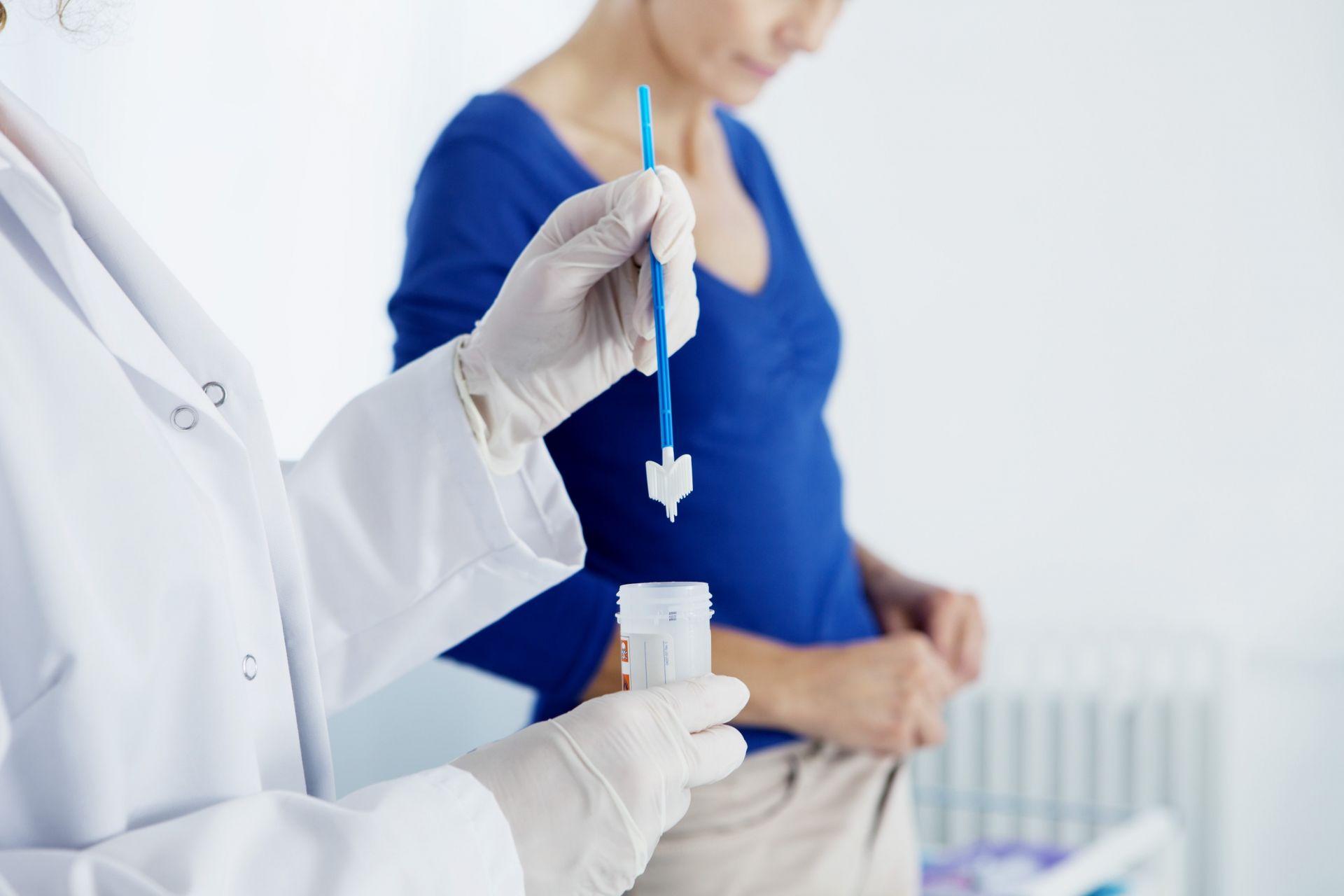
Screening is performed through PAP test and, in some women, the molecular HPV test. The sampling procedure is the same in both cases. The woman sits in her usual gynecological position and the doctor uses the vaginal dilator to locate the cervix.
Then, with the use of special tools (wooden spatula, brush), the doctor takes a sample of cells from the surface of the cervix and the cervical canal (endocervix). Using the latest technique for PAP test (liquid phase cytology - ThinPrep), the sample is transferred to a bottle with a special liquid, which is sent to the cytology laboratory. The advantages of the ThinPrep PAP test include the greater diagnostic accuracy, especially in cases of inflammatory or bloody material, and the possibility of simultaneous molecular detection of HPV in the same sample.
At our Clinic, we exclusively provide ThinPrep PAP test, the most substantial development of the PAP test internationally in recent years.
What exactly is the molecular HPV test and when should it be done?
The PAP test detects possible lesions in cervical cells, which are usually the result of HPV infection. On the other hand, the molecular HPV test allows to directly detect the virus in the cervical cells. When the test is focused on the types of the virus considered high-risk (oncogenic types), it is called HPV test. On the contrary, when it detects all the types of the virus, it is called HPV typing. It is known, however, that low-risk infections do not have the biological potential to cause serious lesions or cervical cancer. Therefore, based on the guidelines of the American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology and the American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, only the determination of HPV oncogenic types should be used when the doctor decides the further follow-up and treatment of the patient. Finally, it is important to identify HPV 16 and 18, since they show the most aggressive behavior.
The HPV test must be done:
- In women, whose PAP test has showed atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASCUS).
- In women aged 30 and over, in combination with the PAP test. Due to the greater diagnostic accuracy of the HPV test, the probability of a woman with both results negative developing severe pre-cancerous lesions or cervical cancer in the next five years is less than 0.5%.
- During the patient follow-up after the treatment of severe precancerous lesions of the cervix.
What kind of preparation is needed before performing a preventive screening for cervical cancer?
Ideally, the woman should avoid vaginal washings, sexual intercourse, or the use of tampons and vaginal creams for two days before the examination. It is also advised not to schedule the test during the menstrual period.